Check Out Our Blog Posts:
-

GOPAL, SINGLETON BILL TO ENCOURAGE USE OF FUEL CELLS PASSES SENATE 37-0
-

Redlands Passenger Rail Project Update – America’s 1st Hydrail >90% Complete
-

Sen. Brad Hawkins’ Bill on Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles Unanimously Passes
-

GTI Preparing to Launch First-of-a-Kind Pilot with Fuel Cell Yard Trucks
-

Senator Charles Schumer Calls on DOE to Support Green Hydrogen Production
-

FAURECIA ACCELERATES ITS ZERO EMISSIONS HYDROGEN STRATEGY IN CHINA
-
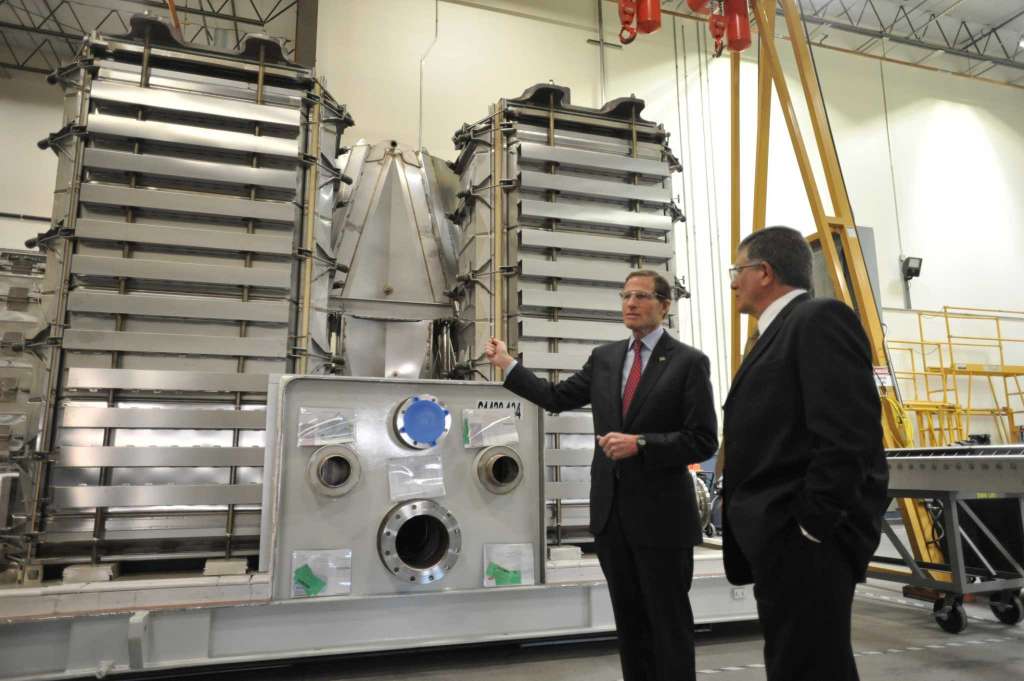

Biden Administration Initiates Energy Effort to Create American Jobs Including Zero Carbon Hydrogen
-
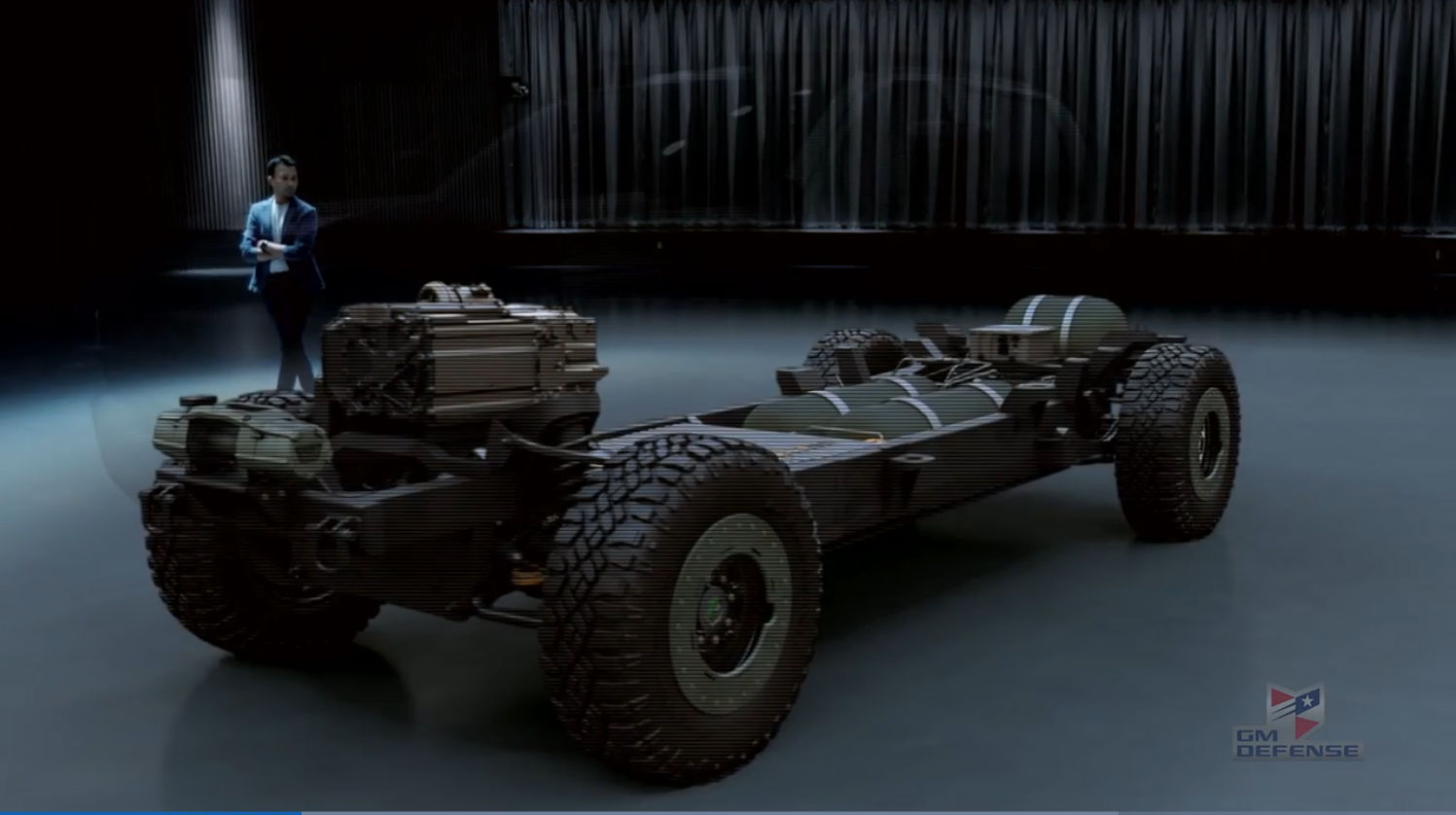

Committee Passes Hawkins Bill Promoting Hydrogen FCEVs
-

Sunnyvale Hydrogen Station Opens
-

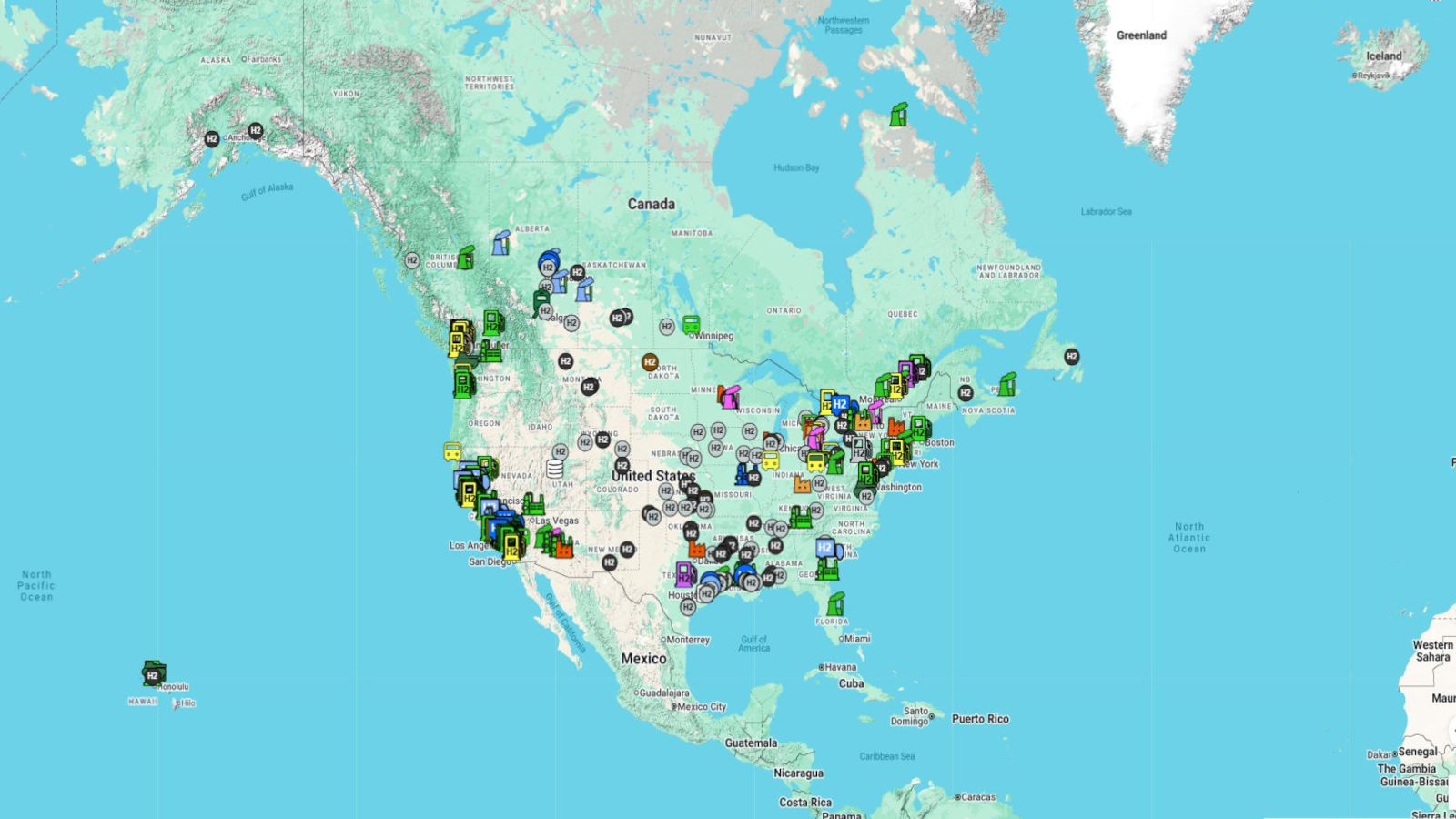
USA & CANADA QUARTERLY H2 INFRASTRUCTURE UPDATE 2020-Q4
-

USA’s Public Retail Hydrogen History: A View from Late 2020
-

USA & CANADA QUARTERLY H2 INFRASTRUCTURE UPDATE 2020-Q3