Could the future of renewable energy lie in a basic household chemical under your kitchen sink? Ammonia might power your household cleaning and fertilize your plants, but it could become an important zero emission energy carrier for moving clean energy around the world economically. Oil & gas, which make up most of our current energy supply, can easily be shipped & stored, but renewable energy that travels through the power grid as electricity cannot. This prevents renewables from becoming a bigger player in the world market of produced & distributed energy. It’s also why researchers are working to streamline current processes to convert solar & wind energy into liquid ammonia which would allow it to be shipped around the world & stored as easily as petroleum products for those hot evenings & cloudy days when the wind isn’t blowing & the sun isn’t shining.
We need to master our ability to create cheap green hydrogen for essential ammonia production even if we leave the BEV-vs-FCEV passenger car debate completely out of the picture. The conventional manufacture of ammonia (NH3) is a dirty process. But without ammonia, we would not be able to produce food for nearly 60% of the world’s population1. Ammonia is made from nitrogen & hydrogen. Nitrogen molecules are separated from the air we breathe and hydrogen is generally derived from either natural gas or coal in a process which creates greenhouse gasses or about 1.8% of CO2 emissions worldwide2. Once you have the nitrogen & hydrogen segregated, the Haber-Bosch process is employed to make ammonia.

Projects are underway around the world that will change how ammonia is manufactured by using renewable solar & wind energy to create the hydrogen from water instead of steam reformed natural gas. The implications of making “green ammonia” are bigger than just fertilizer too. Liquid ammonia is also an energy carrier with a higher energy density (11.5 MJ/liter) than liquid hydrogen (8.5 MJ/liter)3. Ammonia is easier and much cheaper to store & transport than liquid hydrogen because infrastructure & equipment can be used that already exists (e.g. propane infrastructure). While there are many places around the world working on green ammonia pilot plants (Oxford, United Kingdom – Fukashima, Japan – Iberdola, Spain – & more) RMP thinks Australia is the world leader in the large scale pilot manufacture of green ammonia. Australia has abundant renewable energy resources & potential resources available to boost their economy through the manufacture of green ammonia.
Practical Manufacturing of Green Ammonia & Its Energy Storage Potential
There are a number of reasons why Australia is the primary focus of RMP’s first report on green ammonia. Australia is in the spotlight because of its massive resources and investment in renewable solar & wind energy. Australia currently has 95 large renewable energy infrastructure projects that are in construction (or due to start construction soon). These projects will deliver over $19 billion in capital costs, 11,007 MW of new renewable energy capacity and create 13,567 direct jobs4. Each year terawatt hours of electricity are curtailed5 or go to waste because the electricity cannot be used at the time of generation. It’s a problem that has and will continue get worse as more renewable electricity generation capacity comes online.
Battery storage solutions that only last for 24 hours or as peakers are great and serve very important purposes. Battery storage projects also have great payback as short term energy solutions. However, short burst solutions are part of the problem with massive demand for energy as they only satisfy a fraction of what is needed for base-load power over extended durations. We need solutions like ammonia that will have costs scale down as usage scales up because of solar, wind, & hydrogen abundance. Short term battery solutions become too expensive as they scale larger than the peaker size. Batteries also are not the right solution if we need energy for days, weeks, months, and seasons. It is one of the toughest problems to solve with renewable energy that has its highest output during hours when humans don’t need electricity and vice versa. We need a way to store massive amounts of wasted electrical energy so we can have it back when we need it. As more and more renewable energy comes online, cumulative curtailed electricity numbers will continue to climb without the means to store excess generation.
When in liquid form at ambient temperature, ammonia has an energy density of about 3 kWh/liter and if chilled to negative 35 celsius, ammonia’s energy density approaches 4 kWh/liter6. Australia can use their vast renewable resources to achieve economical manufacture, production, and storage of green ammonia by simply buying electrolyzers that turn water into H2 & O2. Australia can be on their way to making more green ammonia with proven technology that is easy to deploy. While ammonia is an absolute societal necessity for agricultural fertilizer in an established world market, it also has even bigger economic potential as a carrier of energy. Energy is a new market for ammonia that will displace oil & gas market share.
The Yara Pilbara Renewable Ammonia Feasibility Study is for a demonstration-scale renewable hydrogen and renewable ammonia production and export facility on the Burrup Peninsula, Western Australia. Yara’s Burrup Peninsula facility currently produces ammonia by using natural gas as a feedstock for its steam methane reforming process, which produces fossil-fuel based hydrogen. The hydrogen is then used to feed an ammonia synthesis process to produce ammonia. Yara is investigating producing renewable hydrogen to feed its ammonia production process, which will reduce emissions produced by the facility.
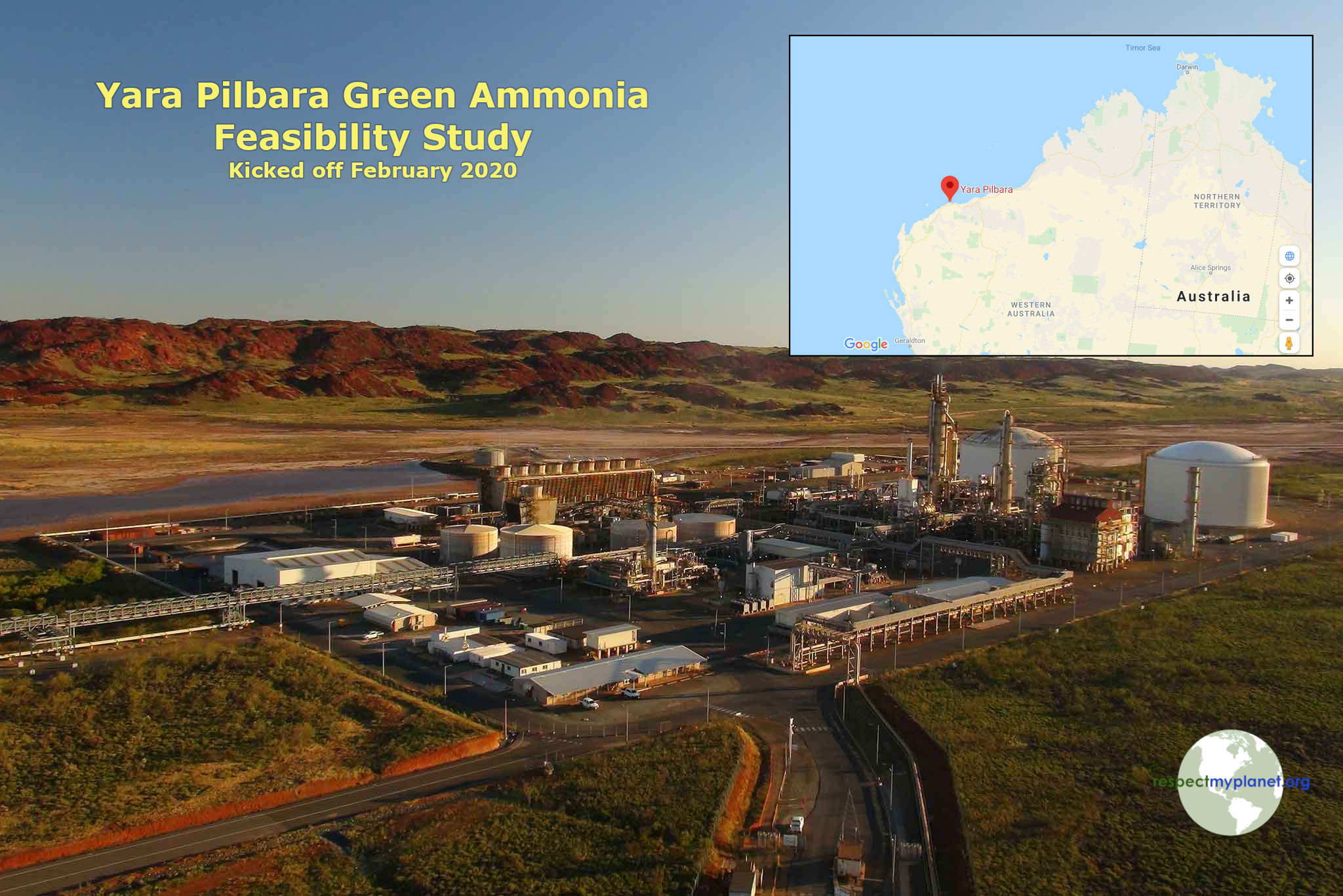
In collaboration with global energy company ENGIE, the Yara Pilbara Renewable Ammonia Feasibility Study will investigate the feasibility of producing renewable hydrogen via electrolysis powered by onsite solar PV. Yara’s objective is that for the demonstration plant, up to three per cent of the hydrogen consumed on site will be renewable hydrogen. The blended hydrogen will subsequently be converted to ammonia and sold for further processing into domestic and international markets. The feasibility study will also investigate using seawater for the electrolyzer.
The feasibility study will help manufacture 30,000 tons of green ammonia that Yara currently would make using fossil fuels. The study will be the first step on the path to achieving commercial scale production of renewable hydrogen and ammonia for export7. In the long term, Yara is aiming to produce hydrogen and ammonia entirely through renewable energy. This approach will allow Yara to avoid any major augmentation to the existing plant and therefore minimise the cost and time needed to produce renewable ammonia.
This project has the potential to ‘unlock’ the value of vast areas of vacant Pilbara land by supporting the development of a new industry that captures solar energy for conversion to hydrogen and other valuable products. Because project’s like Yara Pilbara are likely to surpass feasibility expectations similar to most renewable hydrogen projects, its $3.76m price tag is being funded in part by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) with a $995k investment. The Australian government recognizes how making green ammonia for export can literally transform the continent into an economic powerhouse as renewable generation scales up.
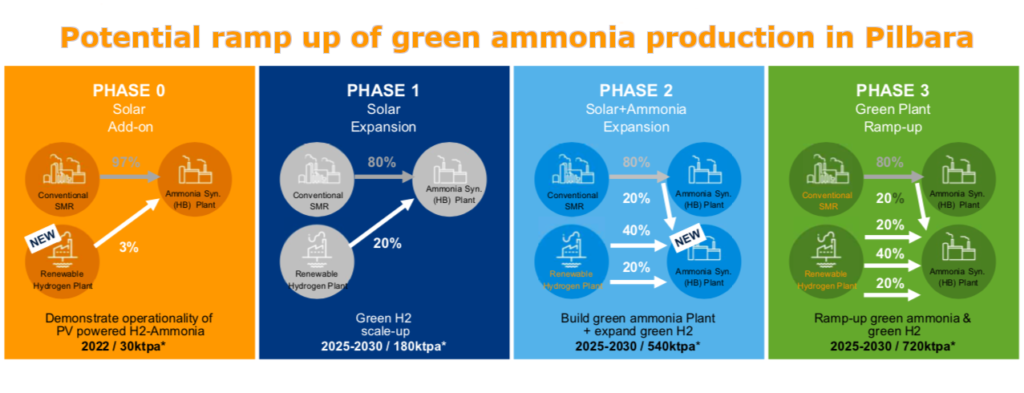
Australia’s government and scientific community want to make green ammonia a significant part of their future economic plans. Australia has renewable resource potential to produce so much more energy than Australians alone can consume which means ammonia has significant export potential which can quickly increase sovereign wealth. A challenge associated with using ammonia as a zero carbon energy carrier is “cracking” the ammonia back into its constituent elements nitrogen & hydrogen. In order to make green ammonia more attractive as an export product, the Aussie’s are attacking this challenge with their top scientific researchers. Enter Australia’s CSIRO.
Cracking Green Ammonia
CSIRO is Australia’s national science research agency. The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), says their mission is to shape the future. CSIRO says it does this by using science to solve real issues to unlock a better future for Australia’s community, economy, & planet. You may remember it was about two years ago to the month (8/08/2018) that CSIRO published a blog post about the successful refueling of a Toyota Mirai & Hyundai Nexo hydrogen fuel vehicle with ultra pure hydrogen “cracked” from ammonia using a brand new membrane technology created by CSIRO scientists. The news humbly/quietly signaled a paradigm change in zero carbon energy for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles like busses, trucks, trains, airplanes, and passenger vehicles. If you have abundant renewable energy to produce green ammonia and a method to crack that ammonia back into hydrogen on demand, you literally have a game changer for green energy.
CSIRO Chief Executive Larry Marshall was one of the first to ride in the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Nexo vehicles powered by ultra-high purity hydrogen, produced in Queensland using CSIRO’s membrane technology. The membrane separates ultra-high purity hydrogen from ammonia, while blocking all other gases. It links hydrogen production, distribution and delivery in the form of a modular unit that can be used at, or near, a refueling station. This means that the transportation and storage of hydrogen – currently a complex and relatively expensive process – is simplified, allowing bulk hydrogen to be transported economically and efficiently in the form of liquid ammonia.
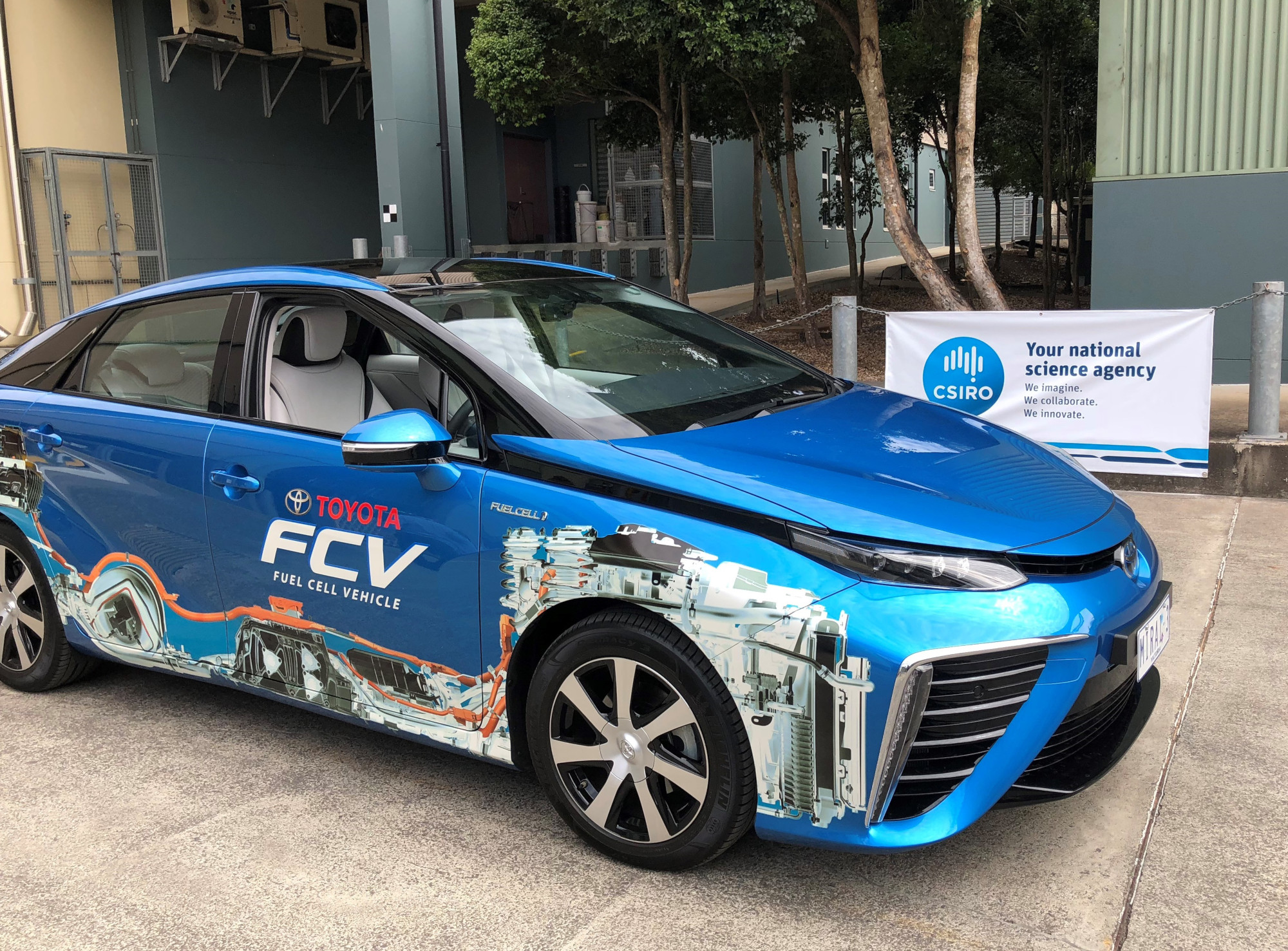

“This is a watershed moment for energy, and we look forward to applying CSIRO innovation to enable this exciting renewably-sourced fuel and energy storage medium a smoother path to market,” Dr Marshall said. BOC Sales and Marketing Director Bruce Currie congratulated CSIRO on the successful refueling of hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles, which proved the effectiveness of CSIRO’s membrane technology from generation, right through to point of use. With this successful demonstration under CSIRO’s belt, the technology will be increased in scale and deployed in several larger-scale demonstrations, in Australia and abroad. CSIRO’s membrane technology will make green ammonia more attractive to foreign consumers who want to import the zero carbon energy carrier into their smog & CO2 belching countries. This is particularly relevant for enormous nearby markets like China, Japan, and South Korea who have committed to hydrogen economies to decarbonize and de-smog their cities.
Worldwide Green Ammonia Distribution Logistics
Green ammonia will be competing with many other forms of energy that are fighting for investment dollars. Ammonia has a couple tricks up its sleeves with regard to affordability & return on investment. One of the key fuels that ammonia will compete with out on the open oceans is Liquified Natural Gas which has a very high volumetric energy content at 6 kWh/liter compared to ammonia’s 3 kWh/liter at ambient temperature or almost 4 kWh/liter if chilled to -35C. RMP created our map of all LNG facilities in the world when Cheniere was granted the USA’s first permit to export LNG in 2011. Green ammonia will have to compete with LNG that has grown significantly since RMP first wrote about Cheniere in August of 2015 just over five years ago. America now has 5 LNG liquefaction facilities permitted for export & built since 2015. These are carefully planned investment decisions on plants that take years to build. Even the F.I.D’s on a new LNG plant can take years because of the risk of investing so much money over such a long horizon.
While LNG liquefaction has received significant investment in the past five years on assets that are expected to deliver for 25 plus year useful lives, LNG is at a severe disadvantage to ammonia for both maritime use & for maritime bunkering. While ammonia has big advantage over all other 100% green energy carriers with energy density, its real secret weapon against grey and potentially “blue” fuels, like LNG, is its ability to use existing infrastructure like that used for LPGs (e.g. propane). Financial investments with the strongest bang for their buck always win. Green ammonia will be a fierce competitor with regard to economic return on investment.

Because ammonia can be liquified at 7.5 bar at ambient temperatures similar to propane & butane, it has an advantage over LNG as a 100% green energy carrier and could potentially hurt LNG investments as shipbuilders might prefer 0% zero emission vessels & cargo. Ammonia easily fits this role of clean energy ambassador to enormous cargo ships with cheaper bunkering costs. Ammonia bunkering costs will be orders of magnitude cheaper than LNG because of the liquefaction trains & cryogenic storage required for LNG. There is great irony here in that for 10 years we have heard that hydrogen suffers from a “chicken or egg” problem but the truth is the chicken or egg problem befalls LNG to a much more significant degree than ammonia which means hydrogen’s chicken or egg problem also could rapidly become yesterday’s story.
For LNG, the dilemma has been that shipowners have been reluctant to make the switch to LNG as bunker fuel in the absence of ports around the world able to supply it. Yet, the development of the required infrastructure is dependent on such demand. As ammonia is already produced and transported in large quantities around the world by ship, bunker supplies could be readily accommodated, though of course it will have to be expanded once the first ammonia powered vessels are realized, says Niels de Vries, a Naval Architect with C-Job Naval Architects in the Netherlands.
“Nowadays the main consumer of ammonia is the fertilizer industry,” he says. “This industry is supplied by ships which carry ammonia in bulk loads of up to 60,000 dwt. The industry’s existing infrastructure could be used to realize bunker locations for ships in the future, and current production offers the possibility of a smooth transition. There are ports available already that could supply the first ships.”

Shipbuilders are/were already ready to make an economic case for using ammonia as low emission fuel by combusting it and scrubbing NOx. But, with ammonia cracking technology like that mentioned by CSIRO that can turn ammonia to hydrogen on demand, you don’t need to combust it because you can use it in a fuel cell which has more than 2x the efficiency of a combustion engine with zero harmful emissions. All of the sudden, the economics you could use to justify ammonia as fuel have just gotten twice as good & your emissions drop to zero. It really bodes well for ammonia as a green energy carrier. Speaking of CSIRO’s technology to crack ammonia into N2 & H2, phys.org just published a recent article August 19, 2020 regarding a new low-cost membrane technology developed by the Korea Institute of Science & Technology (KIST) to decompose ammonia into high purity hydrogen & nitrogen. More evidence top research authorities like CSIRO & KIST are demonstrating scientists around the world are working fast to unlock the potential of green ammonia. You can bet there are some labs in the USA & UK that will be touting some similar breakthroughs soon.

Recent advances in renewable energy technology have set up the new 2020 decade for continued scaling in the manufacture of zero emission ammonia for sustainable energy. Because hydrogen is inexhaustible, abundant, and in every local community, it could mean economies of scale could make hydrogen very cheap as old petroleum infrastructure could be retrofitted for ammonia storage & distribution. Ammonia is already transported by ocean freight by big ships like Vigor’s 508 foot hull Harvest recently built supporting millions of labor hours in America’s pacific northwest Portland area8. The Harvest was built by American workers using over 9,000 tons of American steel & 4,400 tons of equipment. The Harvest has four cargo tanks, each capable of holding 5,500 tons of liquid anhydrous ammonia at very low pressure. This was the first ammonia vessel built in America since 1982! Think about all the jobs & labor hours America could generate to make even more ships like this that transport ammonia safely across our oceans. Speaking of safety, we need to talk about safety & toxicity in more detail.
Ammonia’s risk profile is similar in magnitude to methane or methanol. For ammonia, the main risks are related to health, as ammonia is toxic. Ammonia’s fire risk profile on the other hand is lower. Ammonia can be stored as a liquid either at -34 degrees Celsius at atmospheric pressure (usually applied for large scale applications) or at room temperature at 10 bar (usually applied for small scale applications). RMP’s stated mission as a non-profit 501(c)3 organization is to protect our fresh water resources. Toxic & water are two words that need to always be separate to protect drinking water. How does RMP recommend a toxic substance, ammonia, and reconcile that position with our mission statement of protecting Michigan’s and the world’s fresh water resources?
Reconciling ammonia’s toxicity with RMP’s mission of protecting freshwater
Ammonia is a product necessary for humans to survive. Ammonia is a naturally occurring compound being created in your body’s cells right now as you read this sentence. Ammonia will continue to be manufactured, stored, and transported in the future the same way it is now and has been used in industry for over 100 years. Like all energy carriers & fuels, ammonia is dangerous and must be handled with appropriate safeguards. RMP was founded on protecting fresh water and eliminating the use of fossil fuels. RMP specifically wants to eliminate crude oil from our energy mix first as it causes great harm to our fresh water resources. Crude oil, gasoline, diesel, and other fuel oils contaminate water wherever they are produced, stored, & distributed. Crude oil has environmental remediation costs that drain public budgets & and ruin our environment irreversibly no matter how much we spend to try to clean it up. Famous spills like the Exxon Valdez that happened in April of 1989 are still costing money to clean up today9. That’s just one example of literally thousands of major instances. Right here in our backyards of Michigan, we remember the Enbridge Line 6B pipeline disaster just over ten years ago that RMP wrote about on its 5 year anniversary. Ammonia is different in relation to environmental disasters; it’s not like fossil fuels. While ammonia can cause fish kills on release and can be deadly, its toxicity to the environment is temporary.
As soon as ammonia is released into the environment, it begins neutralizing. Spilled ammonia, while toxic, will quickly dissipate reacting with moisture to form ammonium. Ammonium then quickly binds to negatively charged soil, organic matter, and clays. Ammonium rarely accumulates in soil because bacteria will rapidly convert the ammonium that is not taken up by plant roots into nitrates (nitrification)9. Yes ammonia is toxic & can cause accidents that could turn deadly if they’re not handled safely; this is the same with all fuels. The difference with ammonia is that spill or release events will always be isolated and short term clean ups. When I think of a serious ammonia accident, I’m reminded of when I was young and I would share my scientific theories with my dad. My dad would remind me of La Chatlier’s principle of chemical equilibrium. Ammonia is a good example of something toxic that quickly finds an equilibrium with the environment to form something non-toxic. I’m glad my dad taught me about La Chatlier’s principle because there is going to be FUD surrounding ammonia just like any other fuel we use. RMP knows, no matter what form of energy we use, there will be people who oppose it [viciously].
RMP supports green ammonia as part of the solution of clean renewable energy that is safe for the environment. While dangers exist with ammonia like any other high energy density medium, imagine the flip side: without ammonia nearly 60% of the world’s population would perish from starvation. The possibility of an accident is the risk to pay to avoid certain calamity if there was no ammonia. When the ammonia FUD comes and people say the sky is falling, remember this paragraph. Ammonia has been in use around the world for a century. No one has any reason to panic, but ammonia certainly needs to be handled safely similar to any other fuel we use today.
Here are three bullet points from the CDC’s Frequently Asked Questions page regarding ammonia when it enters the environment:
- Ammonia is found throughout the environment in air, water, soil, animals, and plants.
- Ammonia does not last very long in the environment. It is rapidly taken up by plants, bacteria, and animals.
- Ammonia does not build up in the food chain, but serves as a nutrient for plants and bacteria.
Again, the points listed above are not to diminish the serious toxic & safety hazards associated with ammonia and the importance of following strict safety protocols to prevent injury, death, or fish kills in an accidental release. Ammonia, like all other forms of substantial energy carriers comes with strict safety protocols for manufacture, handling, storage, and distribution.
RMP hopes to have made clear in this article why the leaders and the scientific community in Australia are all in on green hydrogen & piloting green ammonia plants & commercializing technology to crack ammonia into N2 & H2. In less than one week, on August 27 & 28, 2020, the Australian Chapter of the Ammonia Energy Association will host their 2ND Ammonia = Hydrogen 2.0 Conference (virtual this year due to COVID-19). The conference will be hosted from Monash University based in Melbourne Australia on the south coast.
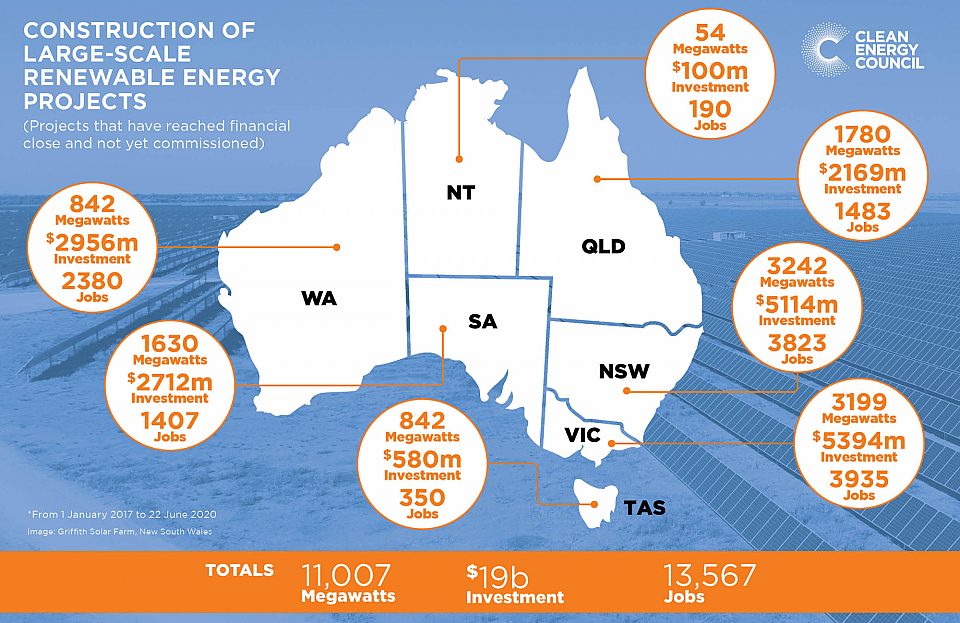
China, Korea, & Japan are all in on green hydrogen and will leverage Australia as a regional trading partner. Australia can provide clean hydrogen energy in a format with a similar economics & logistics to petroleum without the nasty BTEX environmental traits that are silent killers of sovereign wealth. Europe is also expected to be a dominant green ammonia producer according to this article.
Currently, China must invest in all sorts of remote places places in Brazil, Africa, Canada, the USA, and the Middle east to get the coal, crude oil, natural gas, & NGLs it so desperately needs to provide energy & industrial feedstocks for its over 1.3 billion power hungry consumers. What if China could do away with crude oil boondoggles & all those far away countries and get clean green energy from domestic production supplemented by a nearby trading partner like Australia? This is why RMP writes about China’s extensive economic investments into the manufacture of green hydrogen & fuel cells all across China. The exact same goes for Japan & Korea. For those who find interest in the study of chemistry & economics, it’s not difficult to see why so many people around the world are investing sovereign wealth into green ammonia and the hydrogen economy. Green ammonia is a stepping stone on the critical path to a decarbonized society.
Final Conclusion
There are different battery chemistries (NiCd, NiMH, Lead Acid, Li-ion, low cobalt li-ion, lithium polymer) that compete with each other for practical real world applications. There are many different types of fuel cells (PEM, SOFC, PAFC, Alkaline) that also compete with each other for practical applications. All will have roles to play with some more dominant than others just like a sports team made up of great athletes. Similar to the way an artist needs all of the colors in the spectrum on their palette to paint a masterpiece, getting to 100% carbon free energy will need every battery chemistry & fuel cell type to compete with each other on the same canvass of human needs. Because different types of energy are competitors, it does not mean they must be enemies. This is true for humans too.
A lot of human energy goes into arguing about batteries vs hydrogen but clenched fists cannot reach for olive branches. All the battery chemistries & types of fuel cells can compete & coexist in an inclusive arena that understands we will need batteries for some green energy storage & hydrogen for other green stuff. For example, we will need green hydrogen to make green ammonia because ammonia is essential for life. And, as long as we invest in green ammonia to make it cheap & abundant, we should also use it as an energy storage medium with a high energy density that replaces the oil & natural gas we use now. Imagine blue skies & pure drinking water for everyone around the world. Think about so many people here in America and those around the world who should not have to breathe NOx & SOx pollution because they live near a power plant. We have hundreds if not thousands of people now living next to SOx & NOx fumes right here in Detroit near Zug Island & DTE’s River Rouge plant. I know Detroit needs big energy to forge metal & make the cars and trucks that keep America moving, but yuck. Just yuck. We gotta just stop with dirty energy. Ammonia can provide the energy needed to make clean steel in a very cost effective manner here in Detroit, the same way as it can in Australia or Asia.
RMP is a Michigan registered & federal 501(c)3 non-profit organization. RMP writes about and advocates for clean energy that helps protect our freshwater resources here in Michigan and around the world. RMP also makes maps of clean & dirty energy infrastructure using the Google Maps API. Follow us on Twitter and like us on Facebook. Please click here to make a tax deductible donation to RMP to help us keep publishing free content with no ads & energy infrastructure maps.
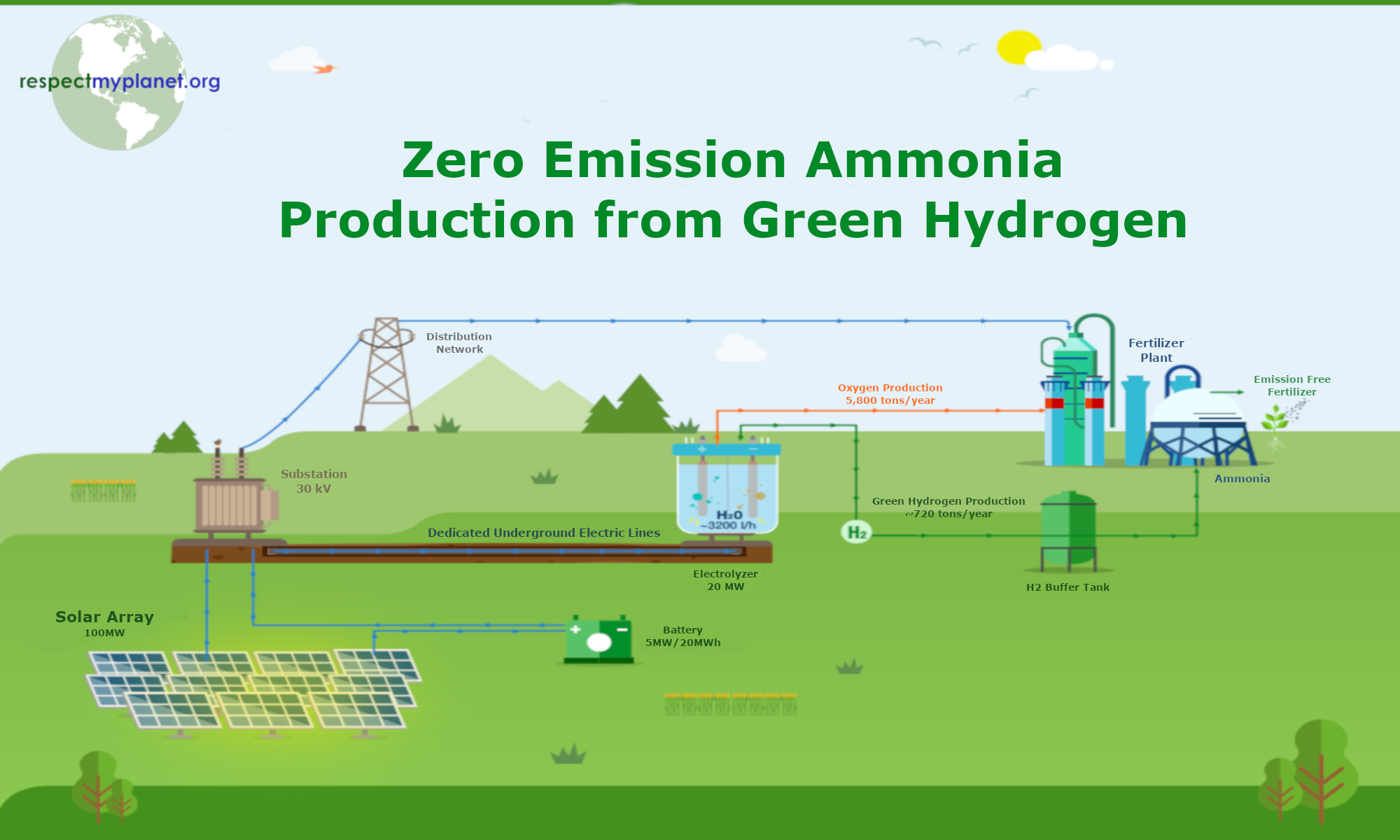
The featured infographic image for this post comes from the Iberdola Spain green ammonia pilot plant. The Iberdola green ammonia plant will be a $177M investment, create 700 jobs, and eliminate 40,000 tons of CO2 each year.
Footnotes:
Footnote #1 – “Yara Green Ammonia” YouTube, uploaded by Yara International November 2019 @ 17 second mark of 1:54 video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cVwDeMPcJio
Footnote #2– The Royal Society, “Ammonia: zero-carbon fertiliser, fuel and energy store” Published February 2020 – pp4. https://royalsociety.org/-/media/policy/projects/green-ammonia/green-ammonia-policy-briefing.pdf
Footnote #3 – Frontiers In Energy Research, “Ammonia as a suitable fuel for fuel cells” last modified August 2014 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenrg.2014.00035/full
Footnote #4 – Clean Energy Council “Project Tracker” last updated June 2020 https://www.cleanenergycouncil.org.au/resources/project-tracker
Footnote #5 – ScienceDirect “Sunny with a Chance of Curtailment: Operating the US Grid with Very High Levels of Solar Photovoltaics” November 2019 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004219303967
Footnote #6– The Royal Society, “Ammonia: zero-carbon fertiliser, fuel and energy store” Published February 2020 – pp7. https://royalsociety.org/-/media/policy/projects/green-ammonia/green-ammonia-policy-briefing.pdf
Footnote #7– Australian Government – Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), “Yara Pilbara Renewable Ammonia Feasibility Study” Published February 2020 https://arena.gov.au/projects/yara-pilbara-renewable-ammonia-feasibility-study/
Footnote #8– Pacific Maritime Magazine, “New Liquefied Ammonia ATB tank barge” Published November 2017 https://www.pacmar.com/story/2017/11/01/features/new-liquefied-ammonia-atb-tank-barge/557.html
Footnote #9– Anchorage Daily News, “Don’t let government give up on Exxon Valdez restoration” Published June 2020 https://www.adn.com/opinions/2020/06/18/dont-let-government-give-up-on-exxon-valdez-restoration/
Footnote #10– Minnesota Department of Agriculture, “Ecological Effects of Ammonia“ Published on the Nitrification Cycle information page. https://www.mda.state.mn.us/ecological-effects-ammonia#:~:text=Ammonia%20in%20Air%20and%20Soil&text=Ammonium%20then%20quickly%20binds%20to,roots%20into%20nitrates%20(nitrification).